Service Manuals, User Guides, Schematic Diagrams or docs for : Advantest R3131 A-D_Block_PCB_Component_Datasheets TMS99C14APEL - GPIB to RS232 Converter
<< Back | HomeMost service manuals and schematics are PDF files, so You will need Adobre Acrobat Reader to view : Acrobat Download Some of the files are DjVu format. Readers and resources available here : DjVu Resources
For the compressed files, most common are zip and rar. Please, extract files with Your favorite compression software ( WinZip, WinRAR ... ) before viewing. If a document has multiple parts, You should download all, before extracting.
Good luck. Repair on Your own risk. Make sure You know what You are doing.
Image preview - the first page of the document
>> Download TMS99C14APEL - GPIB to RS232 Converter documenatation <<
Text preview - extract from the document
10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, 10 - 14 Oct 2005, PO2.047-4 (2005)
GPIB TO SERIAL CONVERTER
Y. Suzuki, K. Agari, M. Ieiri, Y. Katoh, E. Hirose, M. Minakawa, H. Noumi, Y. Sato, H. Takahashi,
M.Takasaki, K. H. Tanaka, A. Toyoda, Y. Yamada, Y. Yamanoi, and H. Watanabe
KEK-IPNS, Tsukuba, Japan
ABSTRACT
In recent years, many PCs and devices with serial communication interface have been adopted in the
lower layer of Accelerator control systems. By the reason of the simplicity, reliability, and the low cost,
the device with serial communication interface will be utilized more and more in accelerator control
systems and physics experimental facilities. As a solution of the method for connecting a large number
of devices with one PC, a GPIB to serial converter has been developed. The converter is equipped with
RS-485 transceiver. The transmitter and receiver are automatically being switched according to the
GPIB commands (talker, listener, EOI). With this converter, 32 RS485 devices can be controlled
through one GPIB node on a multi-drop serial line with maximum length of 1200m. The
communication with serial devise is similarly carried out of the device message of GPIB
communication. As one GPIB controller can be connected directly with 15 GPIB to serial converters,
so the number of connected serial devices becomes 480. For even higher demand to connect devices to
one controller, combinations of the GPIB address converter (presented ICALEPCS2001) and GPIB
bus-extender can be used. With this, the maximum number of devices connectable to one controller
extends to about 28 thousand. The GPIB to serial converter and GPIB address converter will be used
for surveillance of the utility and cross-checking of magnet power supplies in the J-PARC
experimental facilities.
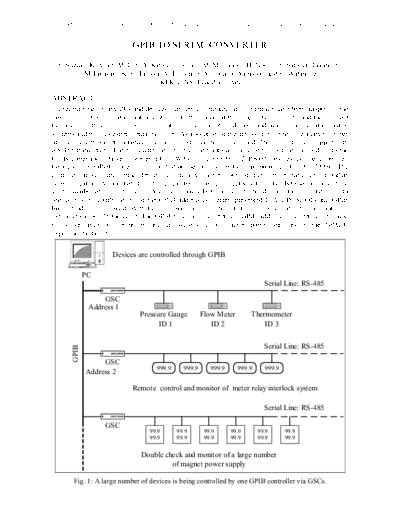
Devices are controlled through GPIB
PC
Serial Line: RS-485
GSC
Address 1
Pressure Gauge Flow Meter Thermometer
ID 1 ID 2 ID 3
Serial Line: RS-485
GPIB
GSC
999.9 999.9 999.9 999.9 999.9
Address 2
Remote control and monitor of meter relay interlock system
Serial Line: RS-485
GSC
99.9 99.9 99.9 99.9 99.9 99.9
99.9 99.9 99.9 99.9 99.9 99.9
Double check and monitor of a large number
of magnet power supply
Fig. 1: A large number of devices is being controlled by one GPIB controller via GSCs.
10th ICALEPCS 2005; Y.Suzuki, K.Agari, M.Ieiri, Y.Katoh, E.Hirose, M.Minakawa, H.Noumi, Y.Sato, H.Taka... 2 of 4
INTRODUCTION
A word ubiquitous is sometimes heard. Actually, in the fields of accelerator control and physics
experiment, there are many digital measuring devices equipped with a micro computer. For example,
many digital meters, digital meter relays, and PLCs, they are used to measure voltage, current,
temperature, pressure, position, and status signal. Those devices are usually equipped with a serial
interface. In order to connect rationally those devices to one PC, some devices are necessary.
Especially, it is important to reduce the number of PCs in a system in order to recover quickly from
power failure, etc. As a solution, a GPIB to Serial Converter (GSC) has been developed. Fig. 1 shows
the position of the GSC in a system. The GSC is connected to a PC or GPIB controller. The advantage
of the system is simplicity, simple maintenance, and low cost.
GPIB TO SERIAL CONVERTER
Hardware
The main parts of GSC are a micro-computer SH2-7045 card and a GPIB interface card. They are
connected with data and address bus and some control wires. Fig. 2 shows the block diagram of GSC.
The SH2-7045 chip has 2 ports of serial line. The serial channel 0 is connected to the RS-485 driver
SP-485. The serial channel 1 is used for the program development. The GSC program is written in
about one thousand lines of the C language, and the code is stored in the flash ROM.
RS-485 Transceiver
Serial port
GPIB
GPIB adapter SH2-7045 Half-duplex line
TMS-c9914
SP485
Driver/Receiver control
Fig. 2: Block diagram of GSC
Control of a RS-485transceiver
When the GPIB adapter TMS99C14 (fig. 2) is addressed as listener, the RS485 driver is enabled.
Data received from the GPIB are sent to the appropriate serial line. When the data end EOI is received,
the RS485 driver is disabled after the send-out shift register is empty. As the RS485 driver is disabled,
the receiver becomes active. The reply data from the serial line is stored in buffer. When the GPIB
interface is addressed as talker, the buffered data is sent out to the GPIB line.
Connection of many serial devices
The example of connecting large number of devices in one PC is shown in fig. 3. The GSC is located
on the GPIB secondary address bus by the use of GPIB address converter (GAC) [1].
PC, GPIB controller GSC
GAC
RS-485 line
GPIB address
converter
GPIB primary bus GPIB secondary bus Digital instrument
Fig. 3: Interfacing a big number of devices via GACs and GSCs to one controller.
10th ICALEPCS 2005; Y.Suzuki, K.Agari, M.Ieiri, Y.Katoh, E.Hirose, M.Minakawa, H.Noumi, Y.Sato, H.Taka... 3 of 4
In case the GSC address is 1, the GAC address is 30, the PC recognizes the GAC as a device of
address 3001. The address ranges of the primary and secondary GPIB bus are 30 each (except
controller). The RS-485 serial line allows up to 32 devices connection. In the configuration of figure 3,
the maximum number of devices to be connected to the RS-485 serial lines becomes about 28
thousand.
Control of serial device through GPIB controller
The program to communicate with serial device through a GPIB controller is shown in figure 4. The
Fig. 4: GSC communication program and execution result.
program is written in VEE (Agilent Technologies). The configuration of devices is similar to figure 3.
The PC is Windows XP. The GAC address is 30, and the GSC address is 1. Therefore the RS-485
serial line is recognized as a device of address 3001(primary address 30, secondary address 01). The
device to be communicate is a digital meter relay address ID=01, model A7111-C Asahi Keiki. The
baud rate is 38400bps (maximum speed of A7111-C). The effective maximum baud rate of the GSC is
115kbps. The program sends A7111-C the data (byte 5: inquiry code, text "01": activates id 01 device,
and CR/LF+EOI), then receives the reply (byte 6: acknowledge code, reply text "01", and CR/LF).
The execution result is shown in the right side of fig. 4.
Assembly
The main parts of GSC are read-mades, CPU board SH2-7045, a GPIB board, a RS485 transceiver,
and power supply, and web-ordered box. The parts are shown in fig. 5.
Fig. 5: Components of the GSC
10th ICALEPCS 2005; Y.Suzuki, K.Agari, M.Ieiri, Y.Katoh, E.Hirose, M.Minakawa, H.Noumi, Y.Sato, H.Taka... 4 of 4
CONCLUSION
Development and test of the GSC have been finished. The GSC is used to monitor and control a large
number digital devices widely distributed in the experimental facilities in J-PARC. Especially, by the
monopolistic hard communication line, stable operation is gained. The GSC is also used as a sub
monitoring system for the magnet power supplies of beam lines, double-checking their operation.
Though the number of components of the sub monitor and control system is large, the maintenance is
easy due to the ROM based GSCs and devices.
REFERENCES
[1] Y. Suzuki et al., "GPIB Address Converter", ICALEPCS'2001, San Jose, California, November
2001.
◦ Jabse Service Manual Search 2024 ◦ Jabse Pravopis ◦ onTap.bg ◦ Other service manual resources online : Fixya ◦ eServiceinfo